Change Language :
Difference between ACME and trapezoidal thread
Lead screws are machine elements and are ideal for converting a rotational movement into a translational movement, for example to drive a door drive. There are many different thread forms and thread types, all of which have their own special features. But what is the difference between the European trapezoidal thread and the American ACME thread? Aren't they the same thing?
Overview:
The European trapezoidal thread (according to DIN103)
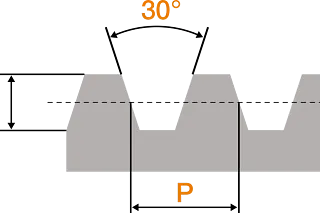
The trapezoidal thread gets its name from its characteristic shape. Seen in cross section, the shape of the thread resembles an isosceles trapezoid with an angle of 15° and a flank angle of 30°. Trapezoidal threads are preferably used as movement threads and can withstand high axial forces. One of the reasons for this is that, in contrast to metric ISO threads, the threads are considerably wider.
Trapezoidal threads are conditionally self-locking. Self-locking depends on the coefficient of friction of the material pairing lead screw/nut, the surface quality and the pitch angle. If the pitch angle is smaller than the friction angle, the screw drive is self-locking.
The European ISO trapezoidal thread is manufactured in metric units in accordance with DIN 103. However, there are small differences in the manufacturing process of the trapezoidal thread with a major impact. On the one hand, the thread flanks are rounded, on the other hand, the thread flanks are sharp-edged.
The American ACME thread (according to ANSI B1.5 2C)
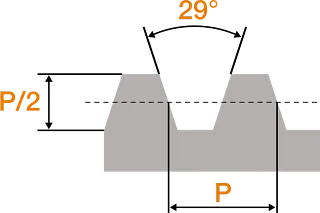
The ACME thread is a thread form developed in American and a further development of the square thread from the 18th century. The square thread was the first choice in the USA at the time. This was because the thread geometry and the 90° flank angle enabled the transmission of movements and high forces with high efficiency. However, due to the flank angle, this thread was also very difficult to manufacture with the production technologies available at the time. The thread geometry was therefore further developed accordingly and designed with a flank angle of 29°. The thread optimisation significantly simplified the manufacturing process. This also had the positive effect of widening the thread root by changing the angle, so that the thread also offers greater strength.
Over time, standards were established for ACME diameters and pitches, all of which were defined using imperial inches for diameter and threads-per-inch units. ACME threads are categorised into specific classes such as 2G, 3G, 2C etc., which have slightly different tolerances.
Example
For example, let's assume that a ¾-ACME lead screw has a principal diameter of 0.75 inches and 10 TPI. To calculate the thread pitch (linear travel in inches per lead screw revolution), we simply divide one inch by the TPI number. In this example, a 10 TPI nut moves 0.10 inches per revolution.
Formula
THREEAD PITCH = 1 / TPI (threads per inch)
Result
ACME 3/8-20 = 0.05 inches per THREAD PITCH
The difference at a glance
With both thread forms, a linear movement is generated by a rotational movement in order to move a heavy load. The American ACME thread form has a flank angle of 29 degrees and the dimensions of the thread are specified in the "imperial" (inch) unit. The European metric ISO trapezoidal thread has a flank angle of 30 degrees and the dimensions of the thread are given in metric units (metres, centimetres and millimetres). The applications for these thread forms are essentially the same. Taking the permissible manufacturing tolerances into account, they can even be interchangeable if the TPI (threads-per-inch) is the same. Typical applications are, e.g., linear drive systems, table height adjusters, vices, bollards, drives for medical analysers, jacks and many more.
👉 Conclusion: Technically, both thread forms are very similar. The main difference lies in the standard, units of measurement and flank angle (30° vs. 29°). Which version is chosen usually depends on whether the end product is intended for the European or the American market. But one thing is clear! In the end, the dryspin technology makes the decisive difference!
| Feature | Trapezoidal thread (DIN 103, imperial) | ACME thread (ANSI, imperial) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin / Standard | Europe, standardised to DIN 103 | USA, standardised to ANSI B1.5 |
| Unit | Metric (mm) | Imperial (inch, TPI = threads per inch) |
| Flank angle | 30° (15° per side) | 29° (14.5° per side) |
| Form | Isosceles trapezoid | Similar to a trapezoid, but flatter angle |
| Self-locking | Limited self-locking (depending on coefficient of friction, surface quality, pitch angle) | Also conditionally self-locking, similar specifications |
| Manufacturing | Rolled or whirled (sharp or rounded flanks) | Optimised for easier production compared to square threads |
| History | Further development for movement threads in Europe | Further development of the square thread in the 18th century in the USA |
| Strengths | Wide threads → high load capacity | Easier production, higher strength due to wider thread base |
| Typical applications | Linear drives, vices, jacks, table adjusters, bollards, medical technology | The same applications, e.g. heavy machinery, tools, drives |
| Interchangeability | Interchangeable under certain conditions, provided that dimensions and tolerances match | The same applies → note metric vs. imperial |
Test our high helix lead screws independently
Consulting
I look forward to answering your questions
Hitech UAB (Distributor)+370 37 323271Write e-mail
Shipping and consultation
In person:
Monday to Friday from 7 am - 8 pm.
Saturdays from 8 am- 12 pm.
Online:
24h
WhatsApp-Service:
Montag – Freitag: 8 – 16 Uhr
